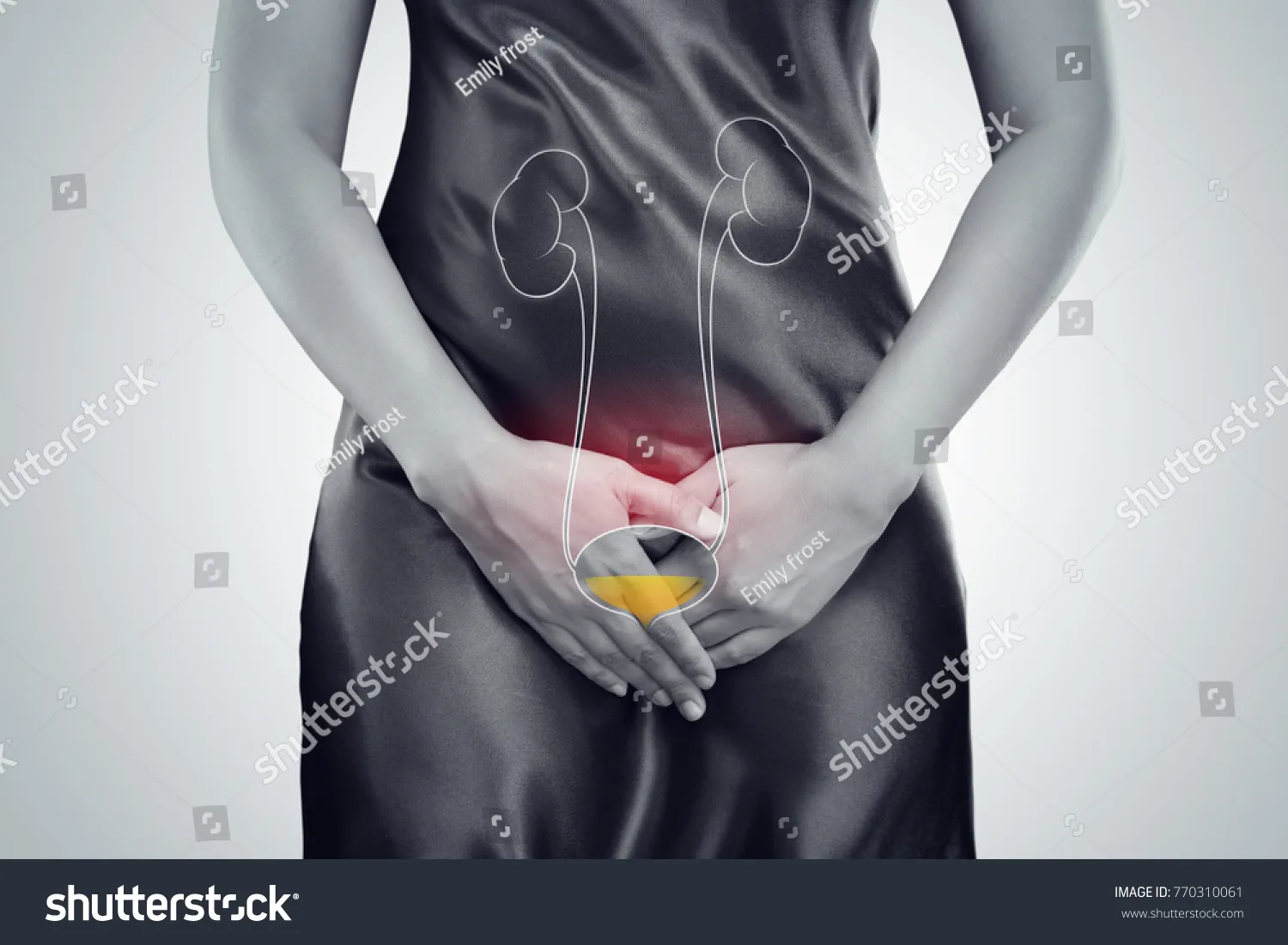
Understanding Honeymoon Cystitis
Honeymoon cystitis, often referred to as honeymoon bladder, is a common type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that many women experience, especially during the early stages of a new relationship. It gets its name because it frequently occurs after an increase in sexual activity. While it can be uncomfortable and inconvenient, understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective prevention methods can help you navigate this experience with confidence and maintain your urinary health. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to honeymoon bladder, helping you understand what it is, how to prevent it, and what to do if you experience symptoms.
What is Honeymoon Cystitis?
Honeymoon cystitis is essentially a UTI that occurs due to increased sexual activity. During sex, bacteria can be introduced into the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. This bacteria can then travel up to the bladder, causing an infection. The frequency and intensity of sexual activity, combined with the potential for friction and irritation, make the bladder more susceptible to infection during this time. It is important to note that while the term ‘honeymoon’ might suggest this only happens during the honeymoon phase of a relationship, it can affect anyone who experiences a surge in sexual activity, regardless of their relationship stage. Recognizing it and taking preventative steps can make a significant difference.
Causes of Honeymoon Cystitis

The primary cause of honeymoon cystitis is the introduction of bacteria into the urinary tract. This can happen during sexual intercourse, as the friction and movement can push bacteria towards the urethra. Additionally, some individuals may be more susceptible to UTIs due to factors like vaginal dryness, which can increase friction, or a lack of vaginal bacteria that normally act to prevent bacterial growth. Certain sexual practices, like anal sex followed by vaginal sex, can also increase the risk due to the introduction of bacteria from the rectum. It’s important to understand that while sexual activity is a primary factor, various other factors can contribute to the development of this condition, so understanding these can enable effective prevention strategies.
Symptoms of Honeymoon Cystitis
The symptoms of honeymoon cystitis are similar to those of any other UTI. Common symptoms include a frequent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is empty or nearly empty. When you do urinate, you might experience a burning sensation or pain. The urine may appear cloudy or have a strong odor, and you might notice blood in your urine. Some individuals may also experience lower abdominal pain or pressure. If the infection spreads to the kidneys, symptoms may include fever, chills, nausea, and back pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly to prevent the infection from worsening and causing further complications.
Preventing Honeymoon Cystitis
Preventing honeymoon cystitis involves several proactive steps to minimize the risk of UTIs. While it is not always possible to prevent the condition entirely, these preventative measures can drastically reduce the likelihood of developing one. Combining several strategies can provide the most effective defense against UTIs, allowing you to enjoy your sexual activity with greater peace of mind. This section outlines several key strategies for preventing this condition, covering everything from hydration to proper hygiene practices. Implementing these tips can help you maintain your urinary health and overall well-being.
Hydration is Key

Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health and is particularly important for preventing UTIs. Adequate hydration helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract, making it more difficult for them to colonize and cause an infection. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day, or more if you are active or live in a warm climate. Increasing your water intake can also help to dilute your urine, making it less irritating to the bladder. Keep a water bottle with you throughout the day, and make it a habit to sip water regularly. This simple practice can significantly reduce your risk of developing a UTI.
Urinate After Sex
One of the most effective ways to prevent UTIs is to urinate after sexual activity. This helps flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sex. Encourage your partner to do the same. Make it a habit to visit the restroom immediately after intercourse. This simple action can help prevent bacteria from attaching to the bladder wall and causing an infection. Consider keeping a small container of water by your bed, just in case you feel the need to urinate. This simple step can make a big difference in preventing honeymoon cystitis. It is a simple yet critical step in safeguarding your urinary health.
Proper Hygiene Practices
Good hygiene is crucial for preventing UTIs. Always wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from the rectum from entering the urethra. Wash the genital area gently with mild soap and water daily, but avoid using harsh soaps, douches, or feminine hygiene products, as these can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and increase the risk of infection. Before and after sex, it is helpful to wash the genital area. Make sure both partners are clean before any sexual activity. These simple hygiene steps can significantly reduce your risk of developing a UTI.
Choosing the Right Lubricant

Using the right lubricant during sex can also help prevent UTIs. Friction during intercourse can irritate the urethra, making it more susceptible to infection. Choose a water-based lubricant over oil-based ones, as oil-based lubricants can trap bacteria. Avoid lubricants containing glycerin or other ingredients that can promote bacterial growth. If you or your partner are sensitive to certain ingredients, read labels carefully to avoid potential irritants. Making informed choices about lubricants can reduce the risk of irritation and bacterial infections, contributing to a more comfortable sexual experience.
Strengthening Your Immune System
A strong immune system is better equipped to fight off infections, including UTIs. Focus on eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to provide your body with the nutrients it needs. Regular exercise can also boost your immune function. Consider taking supplements like vitamin C and probiotics, which can support immune health and help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the body. Managing stress is also crucial, as chronic stress can weaken your immune system. Prioritize getting enough sleep, practicing relaxation techniques, and engaging in activities you enjoy to support your overall well-being.
Other Helpful Strategies
In addition to the tips above, there are other strategies that may help prevent UTIs. Some women find that drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry supplements can help, although the evidence is mixed. D-mannose, a type of sugar, may also help prevent bacteria from attaching to the bladder wall. Consider wearing loose-fitting clothing and cotton underwear, which allows for better air circulation. Avoid holding your urine for extended periods. If you have recurrent UTIs, consult with your doctor about possible preventative treatments, such as low-dose antibiotics or other medications. These methods can work in tandem to minimize the risk of future infections.
When to See a Doctor

While many UTIs can be prevented, it is still important to know when to seek medical attention. If you experience symptoms of a UTI, such as burning during urination, frequent urination, cloudy or bloody urine, or lower abdominal pain, consult your doctor. If you develop a fever, chills, or back pain, these could be signs of a more serious kidney infection, and immediate medical care is necessary. It is always better to err on the side of caution when it comes to your health. Early treatment can prevent complications and promote a quicker recovery.
Diagnosis of a UTI
To diagnose a UTI, your doctor will likely ask about your symptoms and perform a urine test. The urine test typically involves analyzing a sample for bacteria, white blood cells, and red blood cells. In some cases, your doctor may order a urine culture to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection and determine which antibiotics will be most effective. A physical examination might be performed to rule out other potential causes. The diagnosis is usually straightforward. Timely and accurate diagnosis ensures appropriate treatment and minimizes the risk of complications.
Treatment Options for UTIs
The primary treatment for UTIs is antibiotics. The specific antibiotic prescribed will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection and your individual medical history. Always complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if your symptoms improve. Taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help relieve pain and discomfort. Drinking plenty of water is also important to help flush out the infection. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medication to relieve the symptoms of frequent urination and bladder spasms. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully, and be sure to report any side effects. Proper treatment will eliminate the infection and prevent it from recurring.
Long-Term Prevention

Long-term prevention of honeymoon cystitis involves implementing the strategies discussed throughout this article consistently. Stay hydrated, urinate after sex, practice good hygiene, and consider the use of appropriate lubricants. If you experience recurrent UTIs, consult your doctor to explore additional preventative measures, such as low-dose antibiotics or other medications. By being proactive in your approach to urinary health, you can significantly reduce the risk of UTIs and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable lifestyle. Continue practicing the habits that will help reduce the likelihood of future occurrences.